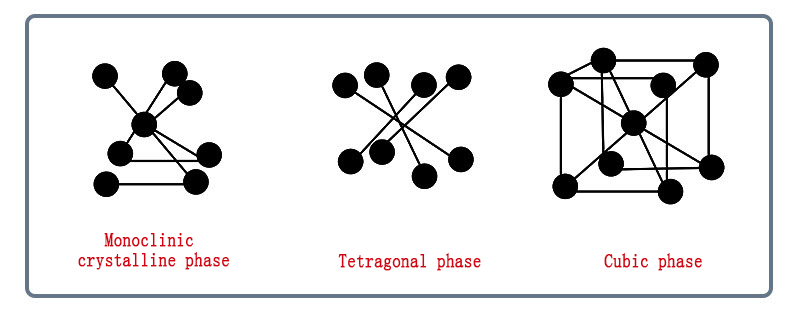
Zirconia ceramics are white, yellow or gray when containing impurities, and generally contain HfO2, which is not easy to separate. There are three crystal states of pure ZrO2 under normal pressure.
■ Low temperature monoclinic (m-ZrO2) ■ Medium temperature tetragonal (t-ZrO2) ■ High temperature cubic (c-ZrO2)
The above three types of crystal exist in different temperature ranges, and there are the following mutual transformation relations:
Characteristics of zirconia ceramics
High-melting-point
Zirconia melting point is: 2715℃, can be used as high temperature refractory material
High hardness, good wear resistance
According to Mohs hardness: sapphire > Zirconia ceramics > Corning Glass > Aluminum magnesium alloy > Tempered glass > polycarbonate
High strength and toughness
The strength of zirconia can reach: 1500MPa
Low thermal conductivity and coefficient of expansion
Among common ceramic materials, its thermal conductivity is the lowest (1.6-2.03W/(m.k)), and the coefficient of thermal expansion is close to that of metal.
Good electrical performance
The dielectric constant of zirconia is 3 times that of sapphire, and the signal is more sensitive.
Application of zirconia ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are widely used in 3C electronics, optical communication, smart wear, biomedical, jewelry, daily life, refractory materials and other fields.
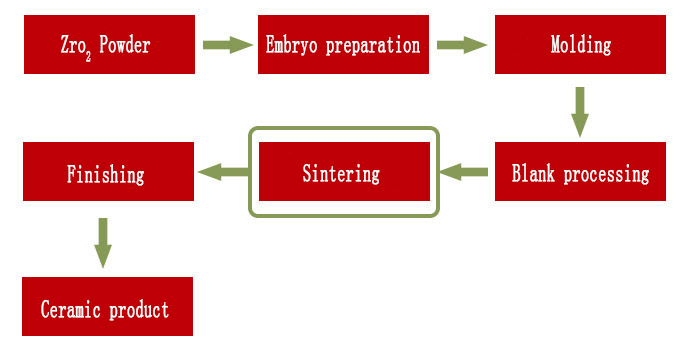
Zirconia ceramic product preparation technology
Sintering is a very important process in the preparation of zirconia ceramics, the quality of sintering will directly affect the ceramic processing, only the sintering temperature is properly adjusted, its embryo body will be perfect. Pressureless sintering is the most commonly used sintering method.
Because pure ceramic materials are sometimes difficult to sintering, under the conditions of performance, some sintering additives are usually introduced to form a partial low melting point of the solid solution, glass phase or other liquid phase, to promote the rearrangement of particles and viscous flow, so as to obtain a dense product, but also reduce the sintering temperature.
Reducing powder size as much as possible is also one of the important measures to promote sintering. Because the finer the powder, the higher the surface energy, the easier the sintering. For ceramic materials and products with common performance requirements, non-pressure sintering is the most convenient and economical sintering method.
Post time: Jul-24-2023