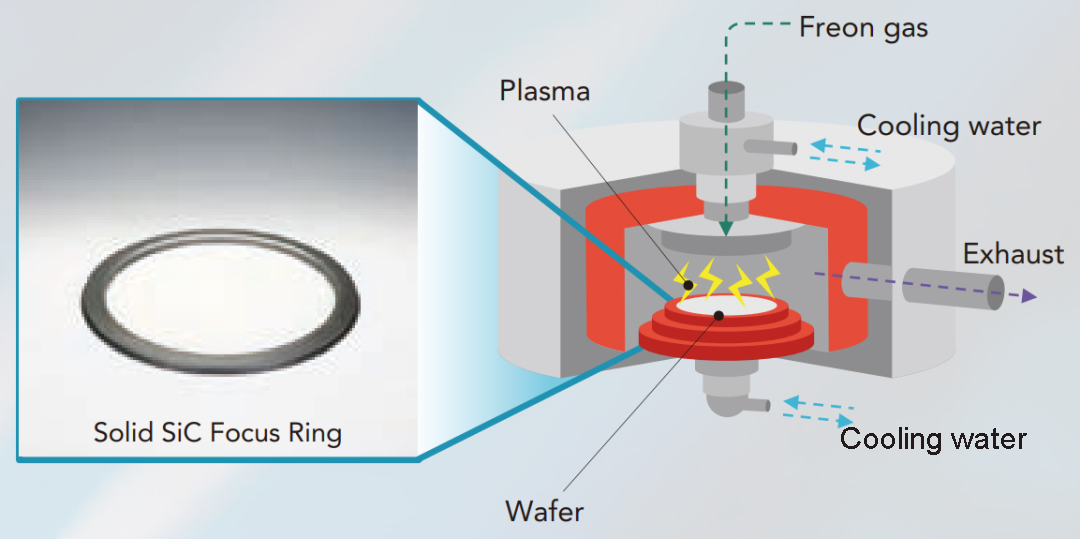
In plasma etching equipment, ceramic components play a crucial role, including the focus ring. The focus ring, placed around the wafer and in direct contact with it, is essential for focusing the plasma onto the wafer by applying voltage to the ring. This enhances the uniformity of the etching process.
Application of SiC Focus Rings in Etching Machines
SiC CVD components in etching machines, such as focus rings, gas showerheads, platens, and edge rings, are favored due to SiC's low reactivity with chlorine and fluorine-based etching gases and its conductivity, making it an ideal material for plasma etching equipment.
Advantages of SiC as a Focus Ring Material
Due to the direct exposure to plasma in the vacuum reaction chamber, focus rings need to be made from plasma-resistant materials. Traditional focus rings, made from silicon or quartz, suffer from poor etching resistance in fluorine-based plasmas, leading to rapid corrosion and reduced efficiency.
Comparison Between Si and CVD SiC Focus Rings:
1. Higher Density: Reduces etching volume.
2. Wide Bandgap: Provides excellent insulation.
3. High Thermal Conductivity & Low Expansion Coefficient: Resistant to thermal shock.
4. High Elasticity: Good resistance to mechanical impact.
5. High Hardness: Wear and corrosion-resistant.
SiC shares silicon's electrical conductivity while offering superior resistance to ionic etching. As integrated circuit miniaturization progresses, the demand for more efficient etching processes increases. Plasma etching equipment, especially those using capacitive coupled plasma (CCP), require high plasma energy, making SiC focus rings increasingly popular.
Si and CVD SiC Focus Ring Parameters:
|
Parameter |
Silicon (Si) |
CVD Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
|
Density (g/cm³) |
2.33 |
3.21 |
|
Band Gap (eV) |
1.12 |
2.3 |
|
Thermal Conductivity (W/cm°C) |
1.5 |
5 |
|
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (x10⁻⁶/°C) |
2.6 |
4 |
|
Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
150 |
440 |
|
Hardness |
Lower |
Higher |
Manufacturing Process of SiC Focus Rings
In semiconductor equipment, CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) is commonly used to produce SiC components. Focus rings are manufactured by depositing SiC into specific shapes through vapor deposition, followed by mechanical processing to form the final product. The material ratio for vapor deposition is fixed after extensive experimentation, making parameters like resistivity consistent. However, different etching equipment may require focus rings with varying resistivities, necessitating new material ratio experiments for each specification, which is time-consuming and costly.
By choosing SiC focus rings from Semicera Semiconductor, customers can achieve the benefits of longer replacement cycles and superior performance without a substantial increase in cost.
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Components
CVD SiC's exceptional thermal properties make it ideal for RTP applications. RTP components, including edge rings and platens, benefit from CVD SiC. During RTP, intense heat pulses are applied to individual wafers for short durations, followed by rapid cooling. CVD SiC edge rings, being thin and having low thermal mass, do not retain significant heat, making them unaffected by rapid heating and cooling processes.
Plasma Etching Components
CVD SiC's high chemical resistance makes it suitable for etching applications. Many etching chambers use CVD SiC gas distribution plates to distribute etching gases, containing thousands of tiny holes for plasma dispersion. Compared to alternative materials, CVD SiC has a lower reactivity with chlorine and fluorine gases. In dry etching, CVD SiC components like focus rings, ICP platens, boundary rings, and showerheads are commonly used.
SiC focus rings, with their applied voltage for plasma focusing, must have sufficient conductivity. Typically made of silicon, focus rings are exposed to reactive gases containing fluorine and chlorine, leading to inevitable corrosion. SiC focus rings, with their superior corrosion resistance, offer longer lifespans compared to silicon rings.
Lifecycle Comparison:
· SiC Focus Rings: Replaced every 15 to 20 days.
· Silicon Focus Rings: Replaced every 10 to 12 days.
Despite SiC rings being 2 to 3 times more expensive than silicon rings, the extended replacement cycle reduces overall component replacement costs, as all wear parts in the chamber are replaced simultaneously when the chamber is opened for focus ring replacement.
Semicera Semiconductor's SiC Focus Rings
Semicera Semiconductor offers SiC focus rings at prices close to those of silicon rings, with a lead time of approximately 30 days. By integrating Semicera's SiC focus rings into plasma etching equipment, efficiency and longevity are significantly improved, reducing overall maintenance costs and enhancing production efficiency. Additionally, Semicera can customize the resistivity of the focus rings to meet specific customer requirements.
By choosing SiC focus rings from Semicera Semiconductor, customers can achieve the benefits of longer replacement cycles and superior performance without a substantial increase in cost.
Post time: Jul-10-2024