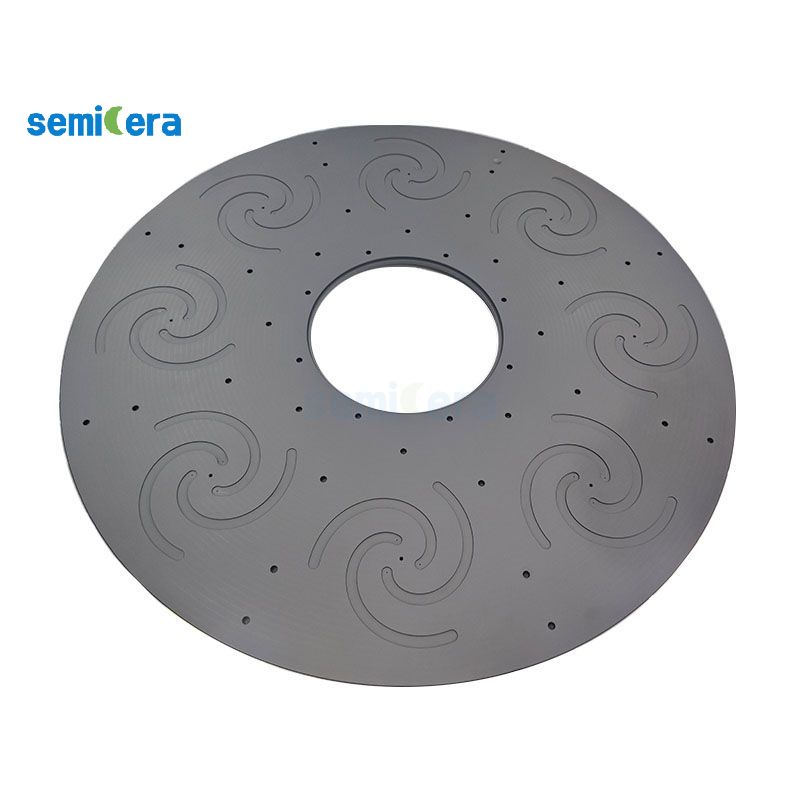
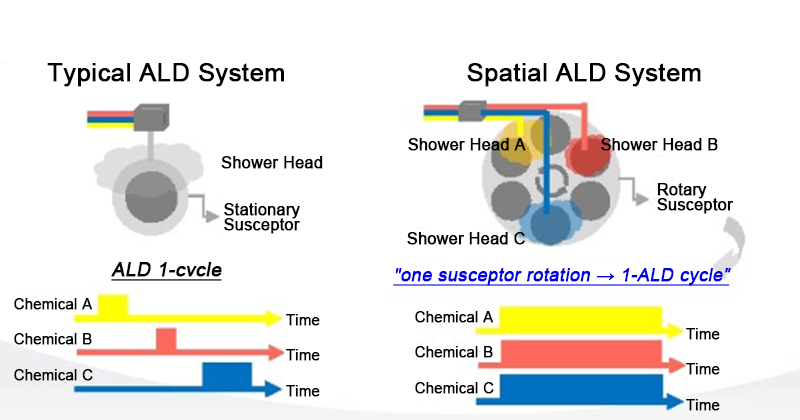
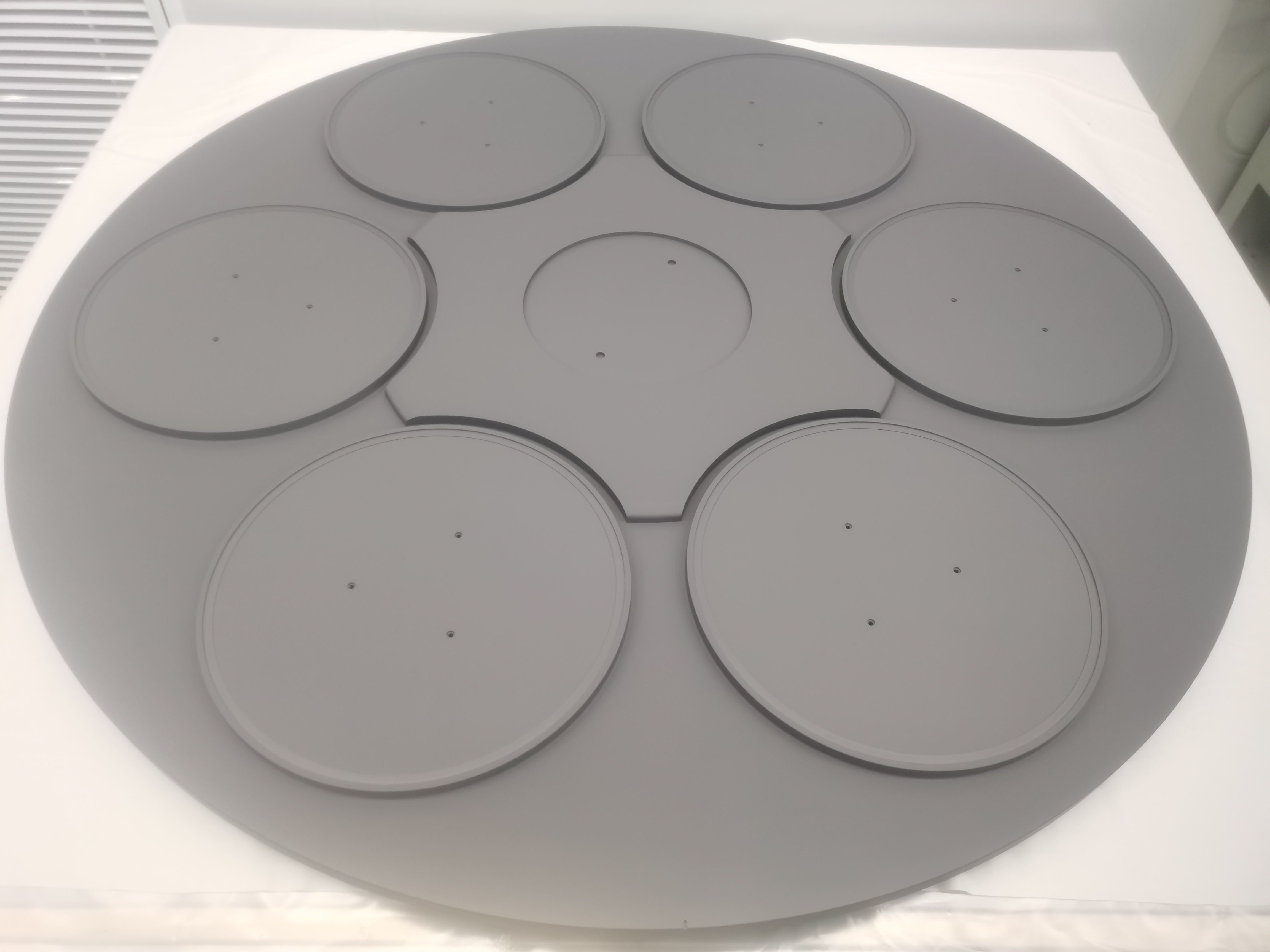
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a chemical vapor deposition technology that grows thin films layer by layer by alternately injecting two or more precursor molecules. ALD has the advantages of high controllability and uniformity, and can be widely used in semiconductor devices, optoelectronic devices, energy storage devices and other fields. The basic principles of ALD include precursor adsorption, surface reaction and by-product removal, and multi-layer materials can be formed by repeating these steps in a cycle. ALD has the characteristics and advantages of high controllability, uniformity, and non-porous structure, and can be used for the deposition of a variety of substrate materials and various materials.

ALD has the following characteristics and advantages:
1. High controllability: Since ALD is a layer-by-layer growth process, the thickness and composition of each layer of material can be precisely controlled.
2. Uniformity: ALD can deposit materials uniformly on the entire substrate surface, avoiding the unevenness that may occur in other deposition technologies.
3. Non-porous structure: Since ALD is deposited in units of single atoms or single molecules, the resulting film usually has a dense, non-porous structure.
4. Good coverage performance: ALD can effectively cover high aspect ratio structures, such as nanopore arrays, high porosity materials, etc.
5. Scalability: ALD can be used for a variety of substrate materials, including metals, semiconductors, glass, etc.
6. Versatility: By selecting different precursor molecules, a variety of different materials can be deposited in the ALD process, such as metal oxides, sulfides, nitrides, etc.